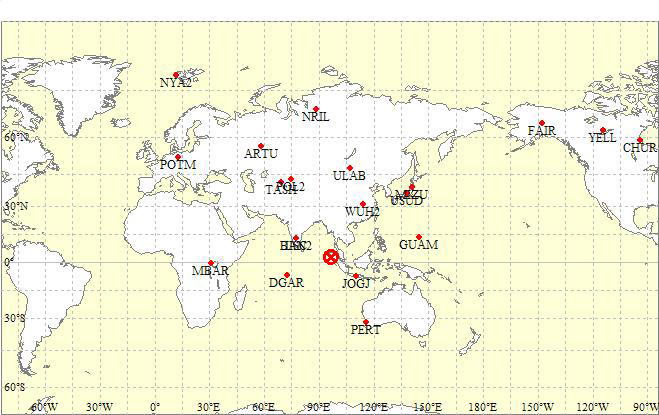
GPS Station Position Map and Epicenter (3.31N, 95.87E, 2004/12/26 0:58:53 UTC)
| GPS高時間分解能精密単独測位(HR-PPP)による地震波観測 Seismic Wave Observation with GPS High-Rate Preceise Point Positioning |
2007/05/13 2006/05/10 |
Home |
GPSキネマティックPPPによる地殻変動観測 5/13追加
GPS Kinematic-PPP (Precise point positioning)
: observation of crustal deformation by using
1-Hz GPS data
セミナ資料 (2006/12) (ppt 6.4MB)
高時間分解能精密単独測位(HR-PPP)による地殻変動観測
High-rate Precise Point Positioning: Detection
of crustal deformation by using 1-Hz GPS
data
Abstruct
Seismic surface waves caused by the Sumatra-Andaman
earthquake are detected by the GPS precise
point positioning (PPP) technique. The precision
of high-rate PPP is usually degraded by the
interpolation error of low-rate satellite
clocks. To solve this problem, 1-Hz satellite
clocks are estimated using the high-rate
observations at GPS stations worldwide. Subsequently
ground motions are analyzed by kinematic-PPP
using the 1-Hz satellite clocks. This technique
is referred to as high-rate PPP (HR-PPP).
By HR-PPP, the seismic waves generated by
the earthquake can be fairly detected. In
contrast to relative positioning conventionally
applied to GPS kinematic analysis, HR-PPP
can efficiently observe the widely distributed
crustal deformations generated by an earthquake
involving long-period waves. To validate
HR-PPP, the analyzed displacements are compared
with the seismograms. The HR-PPP solutions
are in very good agreements with the integrated
velocities measured using broadband seismometers
nearby the GPS stations.
.....................................................
T. Takasu, High-rate Precise Point Positioning: Detection of crustal deformation by using 1-Hz GPS data, GPS/GNSS symposium 2006, Tokyo, 2006, (PDF 594KB)
高時間分解能精密単独測位(HR-PPP)によるスマトラ地震
地震波観測
Observation of seismic wave caused by Sumatra
- Andaman Islands earthquake with HR-PPP
Abstract
The seismic wave of Sumatra - Andaman Islands
earthquake (M9.0) is detected by GPS Precise
Point Positioning (PPP) technique (Zumberge
et al., 1997) with the high-rate GPS observation
data. The precision of the high-rate PPP
is usually degraded by the satellite clock
interpolation error of the precise ephemerides.
In this study, 2-step analysis procedure
is employed to solve the problem. Firstly,
high-rate satellite clocks are estimated
using world-wide IGS network high-rate observations,
with IGS precise satellite orbits and low-rate
clocks. Secondly, using the IGS orbits and
the 1-Hz clocks derived from the first step,
station coordinates are analyzed by the kinematic-PPP.
This strategy is called High-Rate PPP (HR-PPP).
The HR-PPP can fairly detect the displacements
caused by the seismic wave of the earthquake.
The relative positioning, generally used
for the GPS kinematic analysis, is difficult
to separate the movements of the rover and
the reference station and degrades the precision
with the long-baseline. The HR-PPP without
reference stations does not have such problems
and may be effective to analyze the crustal
deformation of the large scale earthquake
involving long period waves. To validate
the observed wave by the HR-PPP, the estimated
displacements are compared with the broad-band
seismographs located near the GPS stations.
In the high-frequency range above 0.01 Hz,
these are consistent. However, the differences
appear below 0.01 Hz. This might be caused
by low-frequency response function of the
seismograph. The long-period noise of the
HR-PPP, caused by the tropospheric correction
error and imperfect antenna phase center
models, is also the possible source of the
low-frequency differences and the future
research and development are necessary to
improve the technique.
高時間分解能GPS観測局データを使って精密単独測位 (PPP, Zumberge et al., 1997) によりスマトラ-アンダマン地震 (M9.0) の地震波観測を行った。高時間分解能PPPにおいては通常精密暦の衛星時計補間誤差による精度劣化が無視できない。本研究ではこの問題を防ぐため、いったん全世界の多数GPS局の高時間分解能観測データを使って衛星時計を推定し、推定した1-Hz 衛星時計を使ってキネマティック-PPPで測位を行う2ステップの解析手法を用いている。この手法を高時間分解能精密単独測位 (HR-PPP) と呼んでいる。HR-PPPによる解析結果では概ね良好に地震表面波による局位置変動が捉えることができた。精密解析に一般的に使われる相対測位によるキネマティックGPS法では基線両端局の位置変動を分離するのが困難でかつ長基線では測位精度が劣化する問題があるが、基準局を必要としないHR-PPPはこの問題がなく、特に地震波継続時間の長い大規模地震による地殻変動の解析手法として有力であると考えられる。HR-PPPによる解析結果の検証のため局位置変動推定値を観測局近隣の広帯域地震計計測値と比較した。HR-PPP解析結果は0.01 Hzより高い周波数帯域では地震計観測波形と良く一致したが、0.01 Hz以下の長周期帯域では違いが目立った。これは長周期波動に対する地震計応答特性の問題に起因している可能性がある。また対流圏遅延補正やアンテナ位相特性モデルの不完全さに起因するHR-PPPの長周期ノイズの影響も大きく、さらに解析手法の改良が必要であると考えられる。
| Station ID | Location | Latitude (deg) | Longitude (deg) | Elevation (m) | Distance from Epicenter | Displacements by HR-PPP | Comparison with seismograph |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JOGJ | Yogyakarta, Indonesia | 7.77S | 110.38E | 136 | 2024km | Fig | - |
| IISC | Bangalore, India | 13.02N | 77.57E | 930 | 2283km | Fig | - |
| BAN2 | Bangalore, India | 13.03N | 77.51E | 918 | 2289km | Fig | - |
| DGAR | Diego Garcia Island, U.K | 7.27S | 72.37E | 10 | 2861km | Fig | Fig |
| WUH2 | Wuhan City, China | 30.53N | 114.36E | 43 | 3586km | Fig | - |
| PERT | Perth, Australia | 31.80S | 115.89E | 45 | 4425km | Fig | - |
| POL2 | Bishkek, Kyrghyzstan | 42.68N | 74.69E | 1755 | 4841km | Fig | Fig |
| TASH | Tashkent, Uzbekistan | 41.33N | 69.30E | 483 | 4979km | Fig | - |
| ULAB | Ulaanbataar, Mongolia | 47.67N | 107.05E | 1649 | 5032km | Fig | - |
| GUAM | Dededo, Guam | 13.59N | 144.87E | 147 | 5503km | Fig | - |
| USUD | Usuda, Japan | 36.13N | 138.36E | 1466 | 5672km | Fig | - |
| MIZU | Mizusawa, Japan | 39.14N | 141.13E | 76 | 6048km | Fig | - |
| ARTU | Arti, Russia | 56.43N | 58.56E | 254 | 6754km | Fig | Fig |
| MBAR | Mbarara, Uganda | 0.60N | 30.74E | 1349 | 7262km | Fig | - |
| NRIL | Norilsk, Russia | 69.36N | 88.36E | 62 | 7351km | Fig | - |
| POTM | Potsdam, Germany | 52.38N | 13.07E | 104 | 9230km | Fig | - |
| NYA2 | Ny-Alesund, Norway | 78.93N | 11.86E | 45 | 9515km | Fig | - |
| FAIR | Fairbanks, USA | 64.98N | 147.50W | 308 | 10889km | Fig | - |
| YELL | Yellowknife, Canada | 62.48N | 114.48W | 208 | 12278km | Fig | - |
| CHUR | Churchill, Canada | 58.76N | 94.09W | 29 | 13076km | Fig | - |

GPS Station Position Map and Epicenter (3.31N,
95.87E, 2004/12/26 0:58:53 UTC)
推定条件
Estimation Parameters
・Analysis Software : GT0.6.2
・Estimation Span : 2004/12/26 0:00-3:00GPST
・Estimation Interval : 1sec
・Estimation Pass : 3pass (Forward/Backward/Forward)+Smoothing
・Estimation Strategy : PPP
・Receiver Position Model : Kinematic
・Fixed Parametes : Orbit/ERP: IGS Final,
Clock: Estimated 1-Hz by GT (see below)
・Estimated Parameters : Receiver Position,
Receiver Clock, Tropos ZTD/Gradients
・Min Elevation : 10deg
・Tropospheric Model : Saastamoinen
・Tropospheric Mapping Function : GMF (Global
Mapping Function)
・Tropospheric Gradient Model : Linear
・Site Displacements : Solid Earth Tide,
Ocean Loading(NAO.99b), Pole Tide
・Satellite/Receiver Antenna PCV : IGS_05.ATX
・Detailed Processing Log : gpsestd.log
Satellite Clock : clk13030_00.clk.gz (5.3MB, Format : RINEX CLK)
・Estimation Interval : 1sec
・Input Parametes : Orbit/Clock/ERP: IGS Final
・Reference Clock : AMC2
・IGS high-rate (1Hz or 0.1Hz) Station List
:
ALGO AMC2 AREQ ARTU BAN2 BOGT BREW CHUR DGAR
FAIR GLPS GODF GOLD GOPE GUAM HLFX HRAO IISC
ISPA KELY KOKB MAD2 MADR MALI MAS1 MATE MBAR
MIZU MKEA MSKU NNOR NRIL OKC2 OUS2 PERT PETS
PIMO POL2 POTM QUIN REDU SANT TASH TIDB ULAB
USN3 USUD VILL WUH2 YELL
HR-PPPによる局位置変動観測
Station displacements observed by HR-PPP
(Time : GPST, Sidereal Filter: applied using day -1 (except for NYA2), Band-Pass Filter: None)
広帯域地震計との比較 (upper : 0.01Hz- , lower
: 0-0.01Hz)
Comparison with broad-band seismographs
| Home |